An Overview of EV Charging Standards and Connector Types
In a perfect world, all electric vehicles would use a universal plug. EV owners wouldn’t have to worry about compatibility when charging, and the process would be seamless.
However, reality is different, making something as simple as charging your EV a potentially tricky task. Although these standards will continue to evolve—especially with the rapid development of modern EVs—here’s a guide to the various current charging standards and how to make owning an electric vehicle more convenient.
EV Charging Levels at a Glance
Just like how the home video market once had VHS and Betamax competing for dominance, EV charging outlets come in a variety of types. Since we're still in the early stages of EV adoption, what's popular today could be outdated tomorrow. The simplest way to understand today's charging standards is by dividing them based on speed.
Level 1
The simplest (and often painfully slow) option is a Level 1 charger, which uses a standard 110/120-volt outlet found in most North American homes. Although it’s slow, these common outlets are widely available and can provide a small boost when needed—adding only 3 to 5 miles of range per hour. This type of charger is usually included with the purchase of an EV.
Level 2
Level 2 chargers run at 240 volts, and can be installed by an electrician with relative ease to existing setups, just like a clothes dryer that runs on electricity. Expect a Level 2 charger to add approximately 25 miles of range per hour.
Level 3
Level 3 chargers are where the charging process becomes impressively fast. Known as DC Fast Chargers, this type of charging (which includes Tesla Superchargers) delivers a powerful DC current of more than 480 volts and 100 amps.
Thanks to this high level of power, Level 3 chargers can recharge a battery in as little as 20 to 30 minutes. While these chargers are rarely found in homes, they are perfect for commercial or public locations where drivers can quickly top off their battery and get back on the road for long-distance trips without a lengthy delay.
The Role of Connectors
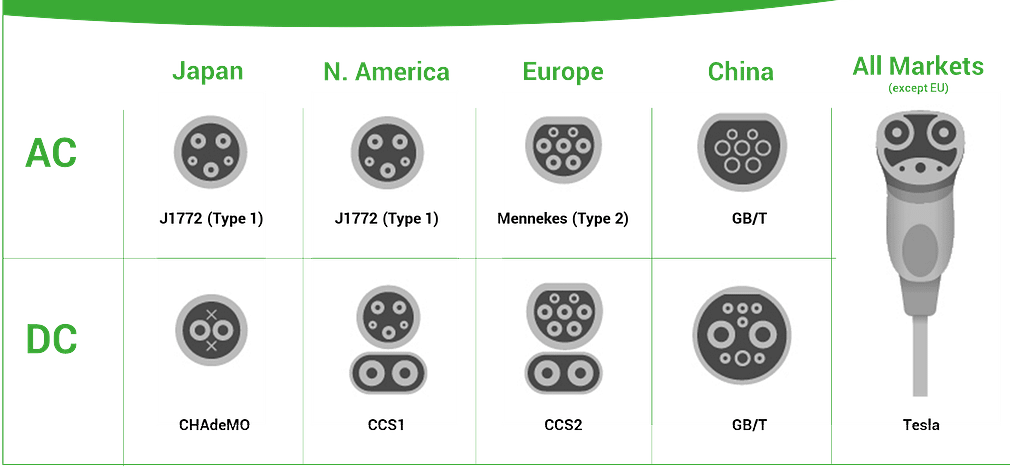
AC (Alternating Current) Connectors
Japan: J1772 (Type 1) - A standard for AC charging primarily used in Japan.North America: J1772 (Type 1) - Similar to Japan, this is the standard AC connector in North America.Europe: Mennekes (Type 2) - A widely used connector for AC charging in Europe.China: GB/T - The Chinese standard for AC charging.
DC (Direct Current) Connectors
Japan: CHAdeMO - A fast-charging protocol that allows for rapid DC charging.North America: CCS1 (Combined Charging System) - A DC fast-charging standard that combines AC and DC charging capabilities.Europe: CCS2 - An upgraded version of CCS1 for DC charging, widely used in Europe.China: GB/T - The standard for DC charging in China.Tesla: Tesla connector - A proprietary connector used by Tesla vehicles for both AC and DC charging.
Understanding Electric Vehicle (EV) Charging Connectors: A Comprehensive Guide
As the world shifts towards sustainable transportation, electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular. With this rise in EV adoption comes the need for a robust and versatile charging infrastructure. At the heart of this infrastructure are the various charging connectors used worldwide. In this blog post, we will explore the different types of EV charging connectors, their specifications, and their significance in the global EV ecosystem.
The Importance of EV Charging Connectors
EV charging connectors are essential components that facilitate the transfer of electricity from charging stations to electric vehicles. They ensure compatibility and safe charging, enabling a seamless experience for EV users. With multiple standards in use globally, understanding these connectors is crucial for manufacturers, infrastructure providers, and consumers alike.
AC Charging Connectors Types
J1772 (Type 1)
Regions:Japan, North America
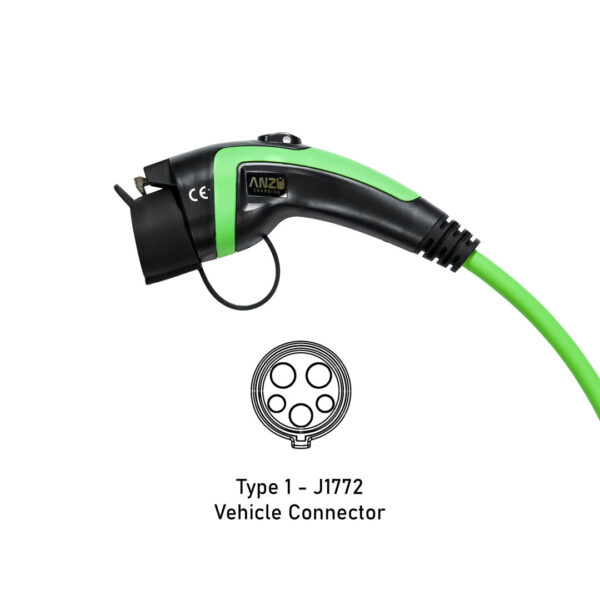

The J1772 connector, commonly referred to as Type 1, is one of the most widely recognized AC charging standards in North America and Japan. Designed for Level 1 and Level 2 charging, it features five pins, allowing it to transfer power at different voltages. Level 1 charging, which utilizes a standard 120V outlet, is typically slow and best suited for overnight charging at home. In contrast, Level 2 charging, which operates at 240V, significantly reduces charging times, making it ideal for public charging stations.
The J1772 connector is versatile and widely adopted, making it compatible with most electric vehicles in North America, including models from major manufacturers such as Chevrolet, Nissan, and Ford. Its widespread use contributes to the development of a reliable charging infrastructure, facilitating the growth of electric vehicle adoption.
Mennekes (Type 2)
Regions:Europe
.png)
The Mennekes connector, or Type 2, is the European standard for AC charging and is rapidly becoming the preferred choice across the continent. With a seven-pin design, the Mennekes connector can support single-phase and three-phase charging, allowing for charging rates of up to 22 kW or more. This capability is particularly advantageous for commercial settings and public charging stations, where faster charging times are essential for high vehicle turnover.
The Mennekes connector is not only compatible with a broad range of electric vehicles sold in Europe but also facilitates the transition to renewable energy sources. By allowing for three-phase charging, the Mennekes connector enables the integration of solar and wind energy into the charging process, further promoting sustainability.
GB/T
Regions:China

The GB/T connector serves as the standard for AC charging in China, with a design tailored to accommodate the unique requirements of the Chinese EV market. It allows for both single-phase and three-phase charging, enabling flexibility in charging options. The increasing adoption of GB/T connectors is closely tied to the rapid growth of the electric vehicle market in China, where government initiatives and consumer demand are driving the expansion of charging infrastructure.
As China's EV landscape evolves, the GB/T connector plays a critical role in ensuring that consumers have access to efficient and reliable charging solutions. Its widespread implementation is essential for meeting the growing demand for electric vehicles and supporting the transition to sustainable transportation.
DC Charging Connectors Types
CHAdeMO
Regions:Japan
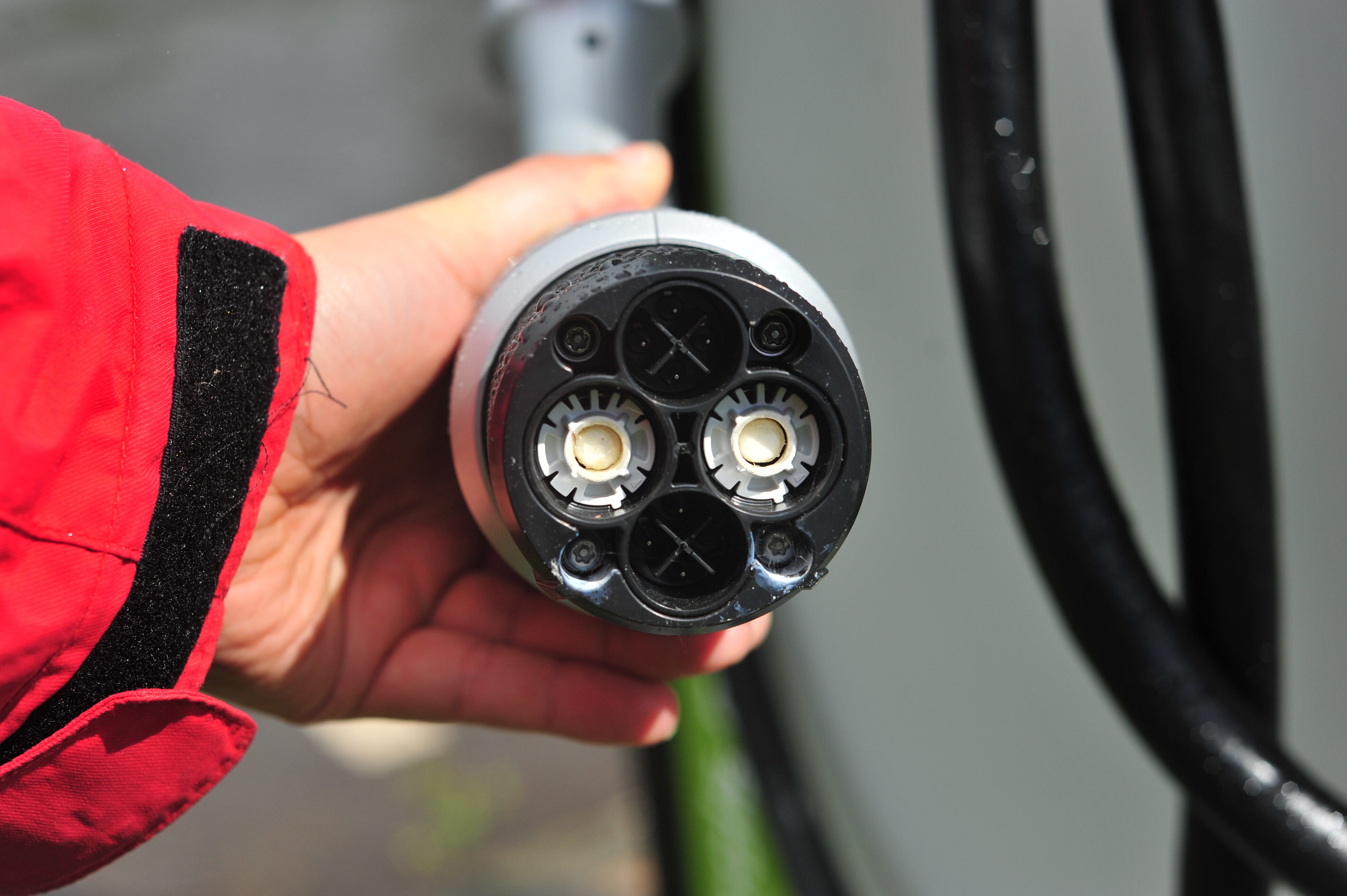

CHAdeMO, which stands for "Charge de Move," is a fast-charging protocol developed in Japan that is specifically designed for DC fast charging. The CHAdeMO connector features two large pins dedicated to DC power, allowing for charging rates of up to 62.5 kW. This rapid charging capability makes CHAdeMO a popular choice among Japanese and European electric vehicle manufacturers.
CHAdeMO is known for its reliability and safety features, which include built-in communication protocols to ensure proper power transfer and vehicle compatibility. Many popular electric vehicles, including those from Nissan and Mitsubishi, utilize the CHAdeMO standard, making it an integral part of Japan's EV charging infrastructure.
CCS1 (Combined Charging System 1)
Regions:North America

CCS1 is a versatile charging standard that combines the functionality of the J1772 connector with additional pins for DC fast charging. This dual capability allows CCS1 to support both AC and DC charging, providing EV users with a comprehensive charging solution. The CCS1 connector can deliver charging rates of up to 200 kW, enabling rapid charging at public charging stations and significantly reducing charging times for electric vehicle owners.
The widespread adoption of CCS1 among major automakers, including BMW, Ford, and Volkswagen, underscores its importance in the North American EV market. The flexibility of CCS1 makes it an attractive option for charging infrastructure providers, as it accommodates a wide range of electric vehicles and enhances the user experience.
CCS2 (Combined Charging System 2)
Regions:Europe

CCS2 is the European counterpart to CCS1, featuring an updated pin configuration that aligns with European charging standards. This connector supports both AC and DC charging, with the capacity to deliver even higher power levels, up to 350 kW. The rapid charging capabilities of CCS2 make it essential for the expansion of charging networks in Europe, particularly as the demand for electric vehicles continues to rise.
The integration of CCS2 into the European EV market is bolstered by the commitment of major automakers and infrastructure providers to support this standard. Its ability to facilitate fast charging will play a significant role in overcoming range anxiety among consumers and promoting the adoption of electric vehicles across the continent.
GB/T
Regions:China
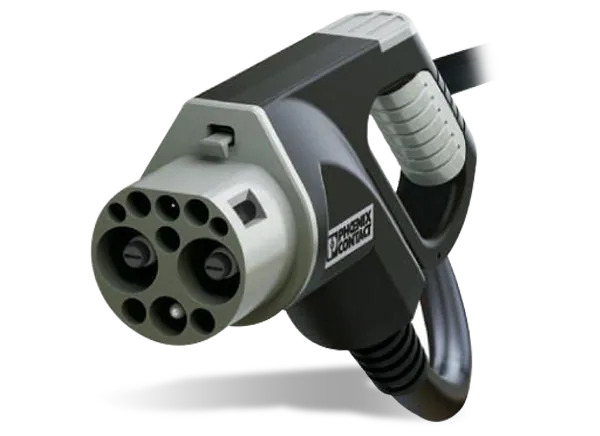

Similar to its AC counterpart, the GB/T connector is also employed for DC fast charging in China. The GB/T design supports high-power charging, enabling rapid charging at various charging stations. As China's electric vehicle market expands, the GB/T connector is becoming increasingly common, providing essential infrastructure for consumers and manufacturers alike.
The standardization of the GB/T connector for both AC and DC charging simplifies the charging process for consumers, ensuring that they have access to a wide range of charging options. This adaptability is critical for meeting the diverse needs of the growing electric vehicle market in China.
Tesla Connector
Regions:All Markets (except EU)
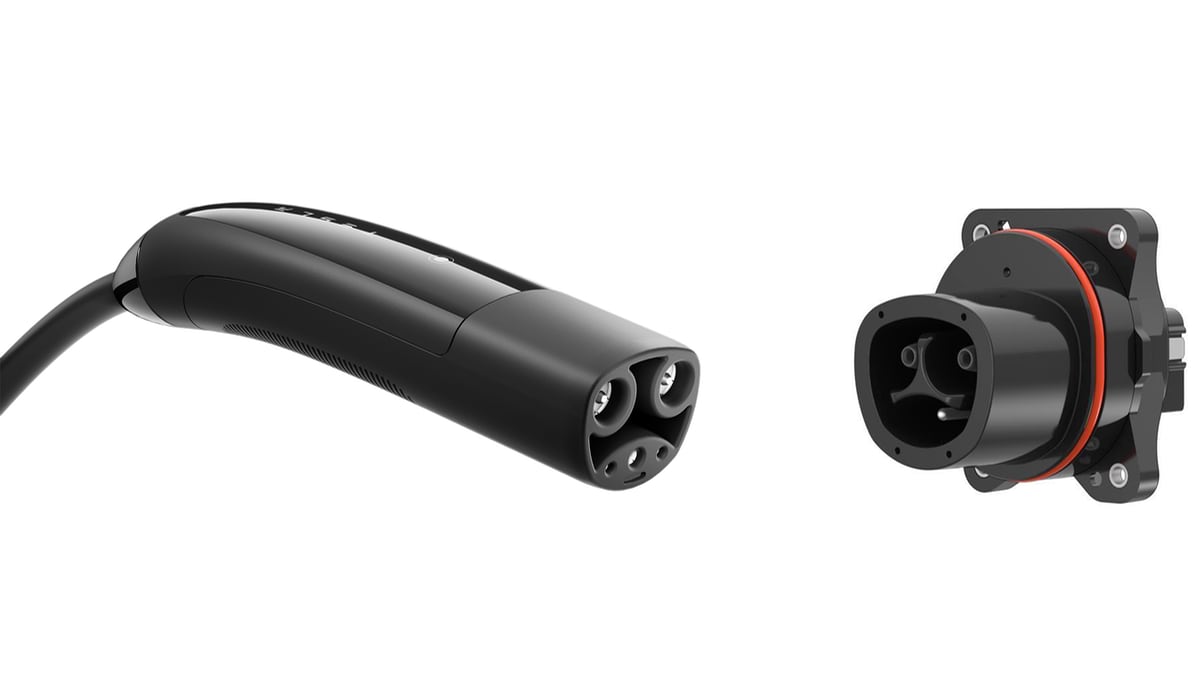

Tesla has developed a proprietary connector that supports both AC and DC charging, allowing Tesla vehicle owners to utilize Tesla Supercharger stations for rapid charging. This unique design provides Tesla users with a seamless charging experience, as the Supercharger network is specifically designed to deliver high charging speeds.
The Tesla connector has become a preferred option among Tesla owners due to its reliability and the extensive Supercharger network available. Tesla's commitment to expanding this network ensures that their customers can enjoy convenient and efficient charging, further solidifying the brand's position in the EV market.
The Future of EV Charging Connectors
As electric vehicles continue to gain popularity, the importance of standardized charging solutions will only increase. While multiple charging standards exist today, ongoing efforts to unify these standards are essential for enhancing compatibility and convenience. Governments, industry leaders, and organizations are collaborating to establish comprehensive charging solutions that cater to the diverse needs of electric vehicle users.
The future of EV charging infrastructure will likely include advancements in technology, such as wireless charging and ultra-fast charging options, further simplifying the charging process. Additionally, integrating renewable energy sources into charging infrastructure will play a vital role in reducing the environmental impact of electric vehicles and promoting sustainability.

.png)